1. Which of the following compounds is a structural isomer of pentane?
a) 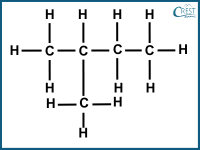
b) 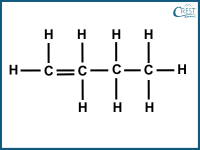
c) 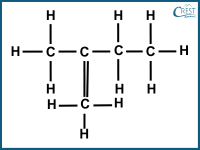
d) 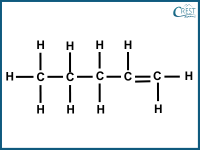
Answer: a) Option a) represents 2-methylbutane which is a structural isomer of pentane. It has the same molecular formula C5H12 but a different arrangement of carbon atoms. In 2-methylbutane, there is a branching or substituent group (methyl group, CH3) attached to one of the carbon atoms in the pentane chain
2. In a laboratory experiment, a chemist is attempting to synthesise an ester. Which of the following combinations of reactants is most likely to produce an ester?
a) CH3COOH (Ethanoic acid) + NaOH (Sodium hydroxide)
b) CH3COOH (Ethanoic acid) + C2H5OH (Ethanol)
c) C2H5OH (Ethanol) + NaOH (Sodium hydroxide)
d) C2H5OH (Ethanol) + C2H4 (Ethene)
Answer: b) Esters are typically synthesised through a reaction known as esterification, where a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst.
In this case:
Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) is a carboxylic acid.
Ethanol (C2H5OH) is an alcohol.
The reaction between ethanoic acid and ethanol produces ethyl ethanoate (CH3COOC2H5), which is an ester.
The chemical reaction is as follows: CH3COOH (Ethanoic acid) + C2H5OH (Ethanol) → CH3COOC2H5 (Ethyl ethanoate, an ester) + H2O (Water)
3. A researcher is studying the solubility of various organic compounds in water. Which functional group in a molecule is most likely to increase its water solubility?
a. Hydroxyl (-OH)
b. Carbonyl (C=O)
c. Carboxyl (-COOH)
d. Alkyl (C-C)
Answer: a) The functional group that is most likely to increase the water solubility of a molecule is the hydroxyl (-OH) group. This is because the hydroxyl group can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Hydrogen bonds are relatively strong intermolecular forces that help molecules dissolve in water. When a molecule contains a hydroxyl group, it can readily interact with water molecules, leading to improved solubility.
4. In a region with very hard water, residents often complain about soap scum buildup in bathtubs and on glass surfaces. Explain the chemical process behind soap scum formation when using soap in hard water.
a) Soap reacts with calcium ions to form insoluble calcium carbonate.
b) Soap reacts with magnesium ions to form a sticky residue.
c) Soap reacts with sodium ions to create a slippery surface.
d) Soap reacts with chloride ions to produce a foamy lather.
Answer: a) Soap scum formation in hard water occurs due to a chemical reaction between the soap (which is typically a sodium or potassium salt of a long-chain fatty acid) and the calcium ions (Ca2+) present in hard water. Hard water contains high concentrations of calcium and magnesium ions.
5. Which allotrope of carbon is characterised by the following properties?
I. Composed of a single layer of carbon atoms.
II. Has excellent electrical conductivity.
III. Possesses exceptional mechanical strength.
IV. Forms a hexagonal lattice structure.
a) Graphite
b) Diamond
c) Graphene
d) Buckminsterfullerene
Answer: c) Graphene, among the carbon allotropes mentioned, is characterised by a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. It possesses excellent electrical conductivity due to delocalised electrons and exceptional mechanical strength. These properties make it unique and suitable for a range of applications.





