1. Which of the following statements is correct based on the experiment where a student took zinc sulphate and copper sulphate in two separate test tubes and then dipped an iron nail in both solutions, observing changes in both test tubes?
a) The iron nail will show visible changes in the copper sulphate solution, but not in the zinc sulphate solution.
b) The iron nail will show visible changes in the zinc sulphate solution, but not in the copper sulphate solution.
c) The iron nail will show visible changes in both the copper sulphate solution and the zinc sulphate solution.
d) The iron nail will not show any visible changes in either the copper sulphate solution or the zinc sulphate solution.
Answer: a) In the experiment, when an iron nail is dipped in a solution of copper sulphate (CuSO4), a displacement reaction occurs. Copper is less reactive than iron, so iron displaces copper from the copper sulphate solution. This results in the formation of a reddish-brown coating of copper metal on the iron nail. On the other hand, when the iron nail is dipped in a solution of zinc sulphate (ZnSO4), no displacement reaction occurs, as zinc is more reactive than iron. Therefore, the iron nail will not show any visible changes in the zinc sulphate solution.
2. Balance the given chemical equation and select the accurate sum of coefficients for the products:
KClO3 → KCl + O2
a) 3
b) 7
c) 5
d) 4
Answer: c) To balance the equation, you need to put a coefficient of 2 in front of KCl and 3 in front of O2 to ensure that the number of atoms is equal on both sides. This results in the balanced equation: 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2, where the sum of coefficients for the products is 2 + 3 = 5.
3. Consider the following equations and choose the correct option:
I. 2FeSO4(s) → Fe2O3(s) + SO2(g) + SO3(g)
II. ZnO + C → + Zn + CO
III. Pb(s) + CuCl2(aq) → PbCl2(aq) + Cu(s)
a) I: Redox Reaction, II: Synthesis Reaction, III: Double Displacement Reaction
b) I: Decomposition Reaction, II: Displacement Reaction, III: Double Displacement Reaction
c) I: Redox Reaction, II: Displacement Reaction, III: Double Displacement Reaction
d) I: Decomposition Reaction, II: Redox Reaction, III: Displacement Reaction
Answer: d) I. FeSO4(s) → Fe2O3(s) + SO2(g) + SO3(g) - This is a decomposition reaction as a single compound breaks down into multiple simpler substances.
II. ZnO + C → + Zn + CO - This is a redox reaction as zinc oxide (ZnO) is reduced to zinc (Zn) by carbon (C).
III. Pb(s) + CuCl2(aq) → PbCl2(aq) + Cu(s) - This is a displacement reaction as lead (Pb) displaces copper (Cu) from copper chloride (CuCl2) to form lead chloride (PbCl2) and copper metal (Cu).
4. Identify A, B, the reducing agent and the oxidising agent in the following reaction.
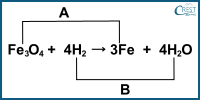
a) A: Reduction, B: Oxidation, Fe3: Oxidising Agent, H2O: Reducing Agent
b) A: Reduction, B: Oxidation, Fe3O4: Oxidising Agent, H2: Reducing Agent
c) A: Oxidation, B: Reduction, Fe3: Reducing Agent, H2: Oxidising Agent
d) A: Oxidation, B: Reduction, Fe3O4: Reducing Agent, H2O: Oxidising Agent
Answer: b) A: Reduction, B: Oxidation, Fe3O4: Oxidising Agent, H2: Reducing Agent
In the given reaction, Fe3O4 is being reduced to Fe while H2 (hydrogen gas) is being oxidised to H2O (water). Therefore:
A: Reduction (undergoing reduction)
B: Oxidation (undergoing oxidation)
Fe3O4: Oxidising Agent (causing oxidation)
H2: Reducing Agent (causing reduction)
5. You want to demonstrate a double displacement reaction that produces a precipitate. Which combination of reactants would most likely result in the formation of a solid precipitate?
a) Sodium chloride (NaCl) and hydrochloric acid (HCl)
b) Potassium nitrate (KNO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
c) Silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium chloride (NaCl)
d) Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH)
Answer: c) The combination that would most likely result in the formation of a solid precipitate is Silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium chloride (NaCl). When silver nitrate reacts with sodium chloride, a double displacement reaction occurs, leading to the formation of silver chloride (AgCl), which is insoluble in water and appears as a white solid precipitate. This reaction is commonly known as the "silver chloride precipitation reaction."


