1. In a population of organisms, why might asexual reproduction be advantageous in rapidly changing or unpredictable environments, while sexual reproduction has its advantages in stable environments?
a) Asexual reproduction produces more offspring.
b) Asexual reproduction leads to greater genetic diversity.
c) Asexual reproduction allows for faster adaptation.
d) Asexual reproduction conserves energy.
Answer: c) Asexual reproduction can be advantageous in rapidly changing or unpredictable environments because it allows for faster adaptation to new conditions. In asexual reproduction, offspring are genetically identical or nearly identical to the parent, which means that beneficial mutations can quickly spread through the population without the need for complex mating processes. This rapid adaptation can help asexual organisms thrive in fluctuating or challenging environments.
2. A botanist conducts an experiment to study the impact of endosperm development on seed germination. They remove the endosperm from a set of seeds and compare their germination rates with intact seeds. What is the expected outcome of this experiment?
a) Seeds without endosperm will germinate faster.
b) Seeds without endosperm will not germinate.
c) Seeds without endosperm will have delayed germination.
d) There will be no difference in germination between the two groups.
Answer: c) The endosperm in seeds serves as a source of nutrients for the developing embryo during germination. When the endosperm is removed from the seeds, the embryo may lack the necessary nutrients to support its initial growth. As a result, seeds without endosperm are likely to experience delayed germination compared to intact seeds that have a source of stored nutrients in the endosperm. While seeds without endosperm may eventually germinate, the initial stages of germination may be slower due to the absence of this nutrient reserve.
3. Select the option that accurately describes the primary functions of the components of the female reproductive system shown in the picture:
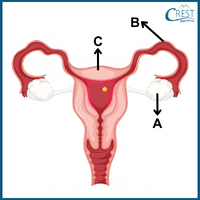
a) A: Ovaries- Egg and hormone production; B: Uterus - Site of fertilisation; C: Fallopian tubes- Implantation of the fertilised egg.
b) A: Ovaries- Egg and hormone production; B: Fallopian tubes- Site of fertilisation; C: Uterus- Implantation of fertilised egg.
c) A: Ova- Egg and hormone production; B: Uterus - Site of fertilisation; C: Fallopian Tubes- Implantation of fertilised egg.
d) A: Ova- Egg and Hormone production; B: Uterus - Implantation of fertilised Egg; C: Oviducts- Site of fertilisation.
Answer: b) Ovaries: Produce eggs (ova) and female sex hormones, estrogen, and progesterone.
Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts): Capture eggs released from the ovaries and serve as the site of fertilisation.
Uterus (Womb): It provides a site for the fertilised egg (zygote) to implant and develop into an embryo and later a fetus during pregnancy.
4. In the absence of fertilisation, what happens to the levels of progesterone and oestrogen during the latter part of the menstrual cycle?
a) They both increase.
b) They both decrease.
c) Progesterone increases, while oestrogen decreases.
d) Progesterone decreases, while oestrogen increases.
Answer: d) In the absence of fertilisation, during the latter part of the menstrual cycle, the corpus luteum, which is a temporary endocrine structure formed from the remnants of the follicle that releases the egg, begins to degenerate. This leads to a significant drop in progesterone levels because the corpus luteum is responsible for secreting progesterone.
As the progesterone levels decrease, oestrogen levels also begin to decline, but then they start to rise again. The combined decrease in progesterone and the subsequent increase in oestrogen trigger the shedding of the uterine lining, resulting in menstruation and marking the start of a new menstrual cycle. This hormonal shift prepares the body for the possibility of a new ovulation and a fresh chance for fertilisation.
5. Which of the following statements about the epididymis are true?
Statement A: The epididymis is where sperm are produced.
Statement B: Sperm mature and are stored in the epididymis.
Statement C: The epididymis connects directly to the urethra.
Statement D: The epididymis secretes seminal fluid.
a) A and C
b) B and D
c) A and B
d) C and D
Answer: b) Statement A is false. The testes, not the epididymis, are responsible for sperm production.
Statement B is true. Sperms mature and are stored in the epididymis.
Statement C is false. The epididymis connects to the vas deferens, not directly to the urethra.
Statement D is true. The epididymis does not secrete seminal fluid, but it is involved in sperm maturation and storage.


