1. How do nymphs differ from adult cockroaches?
a) Nymphs are smaller, wingless versions of adult cockroaches.
b) Nymphs have wings and reproductive organs.
c) Nymphs are brown or black in colour.
d) Nymphs can live for several years.
Answer: a) During the nymph stage, cockroaches are smaller in size compared to adults and do not have fully developed wings or reproductive organs.
2. An experiment is conducted to observe the life cycle of a butterfly. What is the expected order of the stages to be observed?
a) Egg, pupa, caterpillar, adult
b) Pupa, egg, larva, adult
c) Larva, pupa, egg, adult
d) Egg, larva, pupa, adult
Answer:d) The expected order of the stages to be observed in the life cycle of a butterfly is: Egg, larva (caterpillar), pupa (chrysalis), and adult butterfly.
3. Which of the following is a tertiary consumer in a forest food web?
a) Rabbit
b) Hawk
c) Grasshopper
d) Mouse
Answer: b) In a forest food web, a tertiary consumer refers to an organism that feeds on secondary consumers. Among the given options, the hawk is the most likely candidate for a tertiary consumer.
4. Complete the following marine food chain by selecting the suitable option.
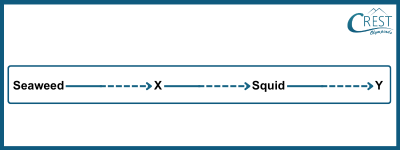
a) X: Shark, Y: Fish
b) X: Fish, Y: Shark
c) X: Whale, Y: Shark
d) X: Fish, Y: Crab
Answer: b) Seaweed serves as a primary producer in the food chain, while squids are considered primary consumers that feed on seaweed. The missing link is the organism that feeds on squids, and in this case, it is a fish. Finally, the top predator in this food chain is a shark, which prey on the fish.
5. Match the organisms with their appropriate levels in a food chain.
| Column I |
Column II |
| 1. Owl |
A) Primary consumer |
| 2. Mushroom |
B) Producer |
| 3. Horse |
C) Secondary consumer |
| 4. Grass |
D) Decomposer |
a) 1:A, 2:D, 3:C, 4:B
b) 1:C, 2:B, 3:A, 4:D
c) 1:C, 2:D, 3:A, 4:B
d) 1:A, 2:C, 3:D, 4:B
Answer: c) Owl: Secondary Consumer
Mushroom: Decomposer
Horse: Primary Consumer
Grass: Producer


