1. A researcher is studying the effect of a specific drug on cell division. They treated a sample of cells with the drug and observed their division rate. Which organelle's activity is likely to be affected by the drug, leading to an impact on cell division?
a) Nucleus
b) Mitochondria
c) Endoplasmic reticulum
d) Lysosomes
Answer: a) The nucleus contains genetic information in the form of DNA, which controls cell division. The drug might affect DNA replication or chromosome segregation, leading to changes in the cell division rate. Mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes are not directly involved in regulating cell division.
2. Identify 1, 6 and 8 from the following image.
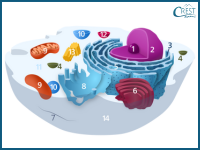
a) 1: Nucleus, 6: Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, 8: Golgi Apparatus
b) 1: Nucleus, 6: Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, 8: Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
c) 1: Nucleolus, 6: Golgi Apparatus, 8: Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
d) 1: Nucleolus, 6: Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, 8: Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Answer: c) 1: Nucleolus, 6: Golgi Apparatus, 8: Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
3. How does the process of osmosis explain the phenomenon of wilting in plants?
a) Water enters plant cells, leading to turgor pressure and rigidity.
b) Excess water leaves plant cells, causing them to shrink and lose rigidity.
c) Water moves out of plant cells, leading to an increase in turgor pressure.
d) Plasmolysis occurs as water diffuses into plant cells.
Answer: b) Wilting in plants occurs when there is a loss of water from the plant cells due to the higher concentration of solutes outside the cells. This causes water to move out of the cells, leading to their shrinkage and loss of rigidity. This phenomenon is a result of osmosis, where water moves from an area of lower solute concentration (inside the cells) to an area of higher solute concentration (outside the cells).
4. In the following question, you will find an assertion and a reason. Select the appropriate option that applies.
Assertion: Mitochondria are unique among cell organelles due to their ability to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Reason: Mitochondria have their own ribosomes and DNA, enabling them to produce proteins.
a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
c) Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
d) Assertion is false, but the Reason is true.
Answer: a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
The Assertion is true as mitochondria indeed generate energy in the form of ATP. The Reason is also true because mitochondria possess their own ribosomes and DNA, allowing them to produce proteins necessary for their functioning. This ability to produce proteins contributes to their uniqueness and their energy-generating capacity.
5. In a laboratory experiment, students investigate the impact of different concentrations of salt solution on the length of potato strips. Which of the following results would support the hypothesis that higher salt concentrations cause water to leave the cells?
a) Potato strips in lower salt concentrations are shorter.
b) Potato strips in higher salt concentrations are shorter.
c) Potato strips in all salt concentrations have the same length.
d) Potato strips in higher salt concentrations are more rigid.
Answer: b) Higher salt concentrations in the surrounding solution create a hypertonic environment, causing water to move out of the potato cells through osmosis. As a result, the potato strips placed in higher salt concentrations will experience a loss of water and become shorter and more shrivelled. This observation supports the hypothesis that higher salt concentrations cause water to leave the cells.


