1. A car of mass 1200 kg accelerates from rest to a velocity of 20 ms-1 in 10 seconds. What is the magnitude of the force applied to the car during this acceleration?
a) 120 N
b) 2400 N
c) 600 N
d) 240 N
Answer: b) To calculate the magnitude of the force applied to the car during its acceleration, we can use Newton's second law of motion, which states that
F = ma
where F is the force applied, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration.
Given:
Mass of the car (m) = 1200 kg
Initial velocity (u) = 0 ms-1
Final velocity (v) = 20 ms-1
Time (t) = 10 s
Acceleration (a) can be calculated using the formula
a = (v−u)/t
Substitute the values:
a = (20 ms-1 − 0 ms-1)/10 s
a = 2 ms-2
Now, use Newton's second law to calculate the force (F):
F = ma
F = 1200 kg × 2 ms-2
F = 2400 N
So, the magnitude of the force applied to the car during its acceleration is 2400 N, and this is the correct answer.
2. A car and a motorcycle are both moving at 60 kmh-1. Which one has greater momentum and why?
a) The car, because it has greater mass.
b) The motorcycle, because it has greater acceleration.
c) Both have the same momentum because they have the same velocity.
d) It depends on the direction of their motion.
Answer: a) Momentum is the product of an object's mass and its velocity. In this case, both the car and the motorcycle are moving at the same velocity of 60 kmh-1. However, the car has a greater mass compared to the motorcycle. Since momentum depends on both mass and velocity, the car will have greater momentum than the motorcycle.
3. A 20 kg mass is attached to one end of a string that passes over a pulley. The other end of the string is pulled by a force of 300 N. Determine the acceleration of the 20 kg mass. (Take g = 9.8 ms-2)
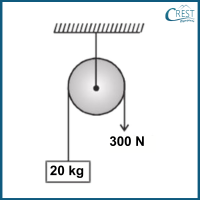
a) 4.8 ms-2
b) 5.2 ms-2
c) 5 ms-2
d) -5.2 ms-2
Answer: b) To solve this problem, we can follow the steps below:
Calculate the force due to gravity acting on the 20 kg mass:
F (gravity) = m x g = 20 kg x 9.8 ms-2 = 196 N
Calculate the net force applied to the 20 kg mass:
Net Force = F (Applied) - F (gravity) = 300 N - 196 N = 104 N
Apply Newton's second law (F=ma) to find the acceleration (a):
Net Force = m x a
104 N = 20 kg x a
a = 104 N/20 kg
a = 5.2 ms-2
4. After applying a strong upward force, a student launches a ball vertically into the air. What is the accurate statement regarding the ball's condition at the peak of its trajectory?
a) The ball has zero acceleration and zero velocity.
b) The ball has zero acceleration but a non-zero velocity.
c) The ball has a non-zero acceleration and a non-zero velocity.
d) The ball has a non-zero acceleration but zero velocity.
Answer: d) At the highest point of its trajectory, the ball reaches its maximum height and momentarily comes to a stop before reversing direction and descending. At this point, its velocity is zero, but its acceleration due to gravity is still acting on it, even though it's in the opposite direction.
5. Two balls, A and B, collide and bounce off each other. Ball A has a mass of 0.5 kg and was initially moving at 4 ms-1 to the right, while ball B has a mass of 0.8 kg and was initially at rest. After the collision, ball A moves at 1 ms-1. What is the velocity of ball B after the collision?
a) 2.0 ms-2
b) 4.4 ms-1
c) 2.5 ms-2
d) 1.9 ms-1
Answer: d) To solve this problem, we can apply the law of conservation of momentum. According to this law, the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision in the absence of external forces.
Initial total momentum = Final total momentum
Let's calculate the initial total momentum of the system:
Initial momentum of ball A = mass of A × initial velocity of A
Initial momentum of A = 0.5 kg × 4 ms-1 = 2 kg ms-1
Initial momentum of ball B = mass of B × initial velocity of B
Initial momentum of B = 0.8 kg × 0 ms-1 = 0 kg ms-1
Initial total momentum = 2 kg ms-1 + 0 kg ms-1 = 2 kg ms-1
Now, let's calculate the final total momentum of the system after the collision:
Final momentum of ball A = mass of A × final velocity of A
Final momentum of A = 0.5 kg × 1 ms-1 = 0.5 kg ms-1
Final momentum of ball B = mass of B × final velocity of B
Let's assume the final velocity of ball B is "v" ms-1.
Final momentum of B = 0.8 kg × v = 0.8v kg ms-1
Final total momentum = 0.5 kg ms-1 + 0.8v kg ms-1 = 0.8v + 0.5 kg ms-1
According to the law of conservation of momentum, initial total momentum = final total momentum:
2 kg ms-1 = 0.8v + 0.5 kg ms-1
Now solve for "v":
2 kg ms-1 - 0.5 kg ms-1 = 0.8v
1.5 kg ms-1 = 0.8v
v = 1.5 kg ms-1 / 0.8
v ≈ 1.875 ms-1
The velocity of ball B after the collision is approximately 1.9 ms-1.


