Solved Questions on Triangle and its Properties
1. What is the sum of exterior angles of the triangle ABC?
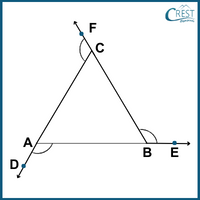
a) 180°
b) 270°
c) 300°
d) 360°
Answer: d) 360°
Explanation: Let interior angles be x°, y° and z°, respectively.
Then, exterior angles are (180 − x)°, (180 − y)° and (180 − z)° respectively.
The labelled diagram is shown as
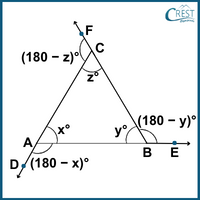
Sum of interior angles of △ABC = x° + y° + z° = 180°
Sum of exterior angles of △ABC = (180 − x)° + (180 − y)° + (180 − z)°
= 180° − x° + 180° − y° + 180° − z°
= 180° + 180° + 180° − x° − y° − z°
= 180° + 180° + 180° − (x° + y° + z°)
= 180° + 180° + 180° − 180°
= 360°
2. Which of the following conditions holds true for △BAT if line segment AQ is the bisector of ∠A and line segment AP is perpendicular to line segment BT?
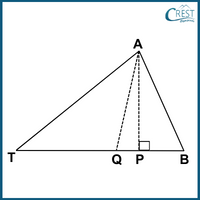
a) ∠PAQ = ∠ABT − ∠ATB
b) ∠PAQ = 1⁄2 (∠ABT − ∠ATB)
c) ∠PAQ = 1⁄3 (∠ABT − ∠ATB)
d) ∠PAQ = 1⁄4 (∠ABT − ∠ATB)
Answer: b) ∠PAQ = 1⁄2 (∠ABT − ∠ATB)
Explanation: In △BAT,
∠TAQ = ∠BAQ [Line segment AQ is the bisector of ∠A.]
∠APB = ∠APQ = 90° [Line segment AP is perpendicular to line segment BT.]
In △BAQ,
∠AQT = ∠BAQ + ∠ABQ [Exterior angle is the sum of two opposite interior angle.]
In △ATQ,
∠TAQ + ∠ATQ + ∠AQT = 180° [Sum of interior angle of a triangle is 180°.]
⇒ ∠TAQ + ∠ATQ + (∠BAQ + ∠ABQ) = 180° [Put ∠AQT = ∠BAQ + ∠B]
⇒ ∠TAQ + ∠ATQ + (∠TAQ + ∠ABQ) = 180° [Put ∠TAQ = ∠BAQ]
⇒ 2∠TAQ + ∠ATQ + ∠ABQ = 180°
⇒ 2∠TAQ = 180° − ∠ATQ − ∠ABQ
⇒ ∠TAQ = 1⁄2 (180° − ∠ATQ − ∠ABQ)
∴ ∠TAQ = 90° − 1⁄2 ∠ATQ − ½ ∠ABQ …………………(i)
∠AQP = ∠TAQ + ∠ATQ [Exterior angle is the sum of two opposite interior angle.]
In △APQ,
∠PAQ + ∠AQP + ∠APQ = 180° [Sum of interior angle of a triangle is 180°.]
⇒ ∠PAQ + ∠AQP + 90° = 180° [Put ∠APQ = 90°]
⇒ ∠PAQ + ∠AQP = 90°
⇒ ∠PAQ + (∠TAQ + ∠ATQ) = 90° [Put ∠AQP = ∠TAQ + ∠ATQ]
⇒ ∠PAQ + 90° − 1⁄2 ∠ATQ − 1⁄2 ∠ABQ + ∠ATQ = 90° [From (i)]
⇒ ∠PAQ = 90° − 90° + 1⁄2 ∠ATQ + 1⁄2 ∠ABQ − ∠ATQ
⇒ ∠PAQ = 1⁄2 ∠ABQ + 1⁄2 ∠ATQ − ∠ATQ
⇒ ∠PAQ = 1⁄2 ∠ABQ − 1⁄2 ∠ATQ
∠ABQ and ∠ABT is the same angle.
∠ATQ and ∠ATB is the same angle.
∴ Hence, ∠PAQ = 1⁄2 (∠ABT − ∠ATB)
3. Which of the following conditions is true for the quadrilateral ABCD?
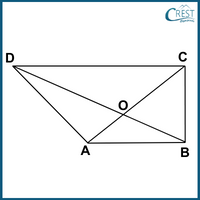
a) DC + DA+ BA + BC > 2(CA + BD)
b) DC + DA + BA + BC < 2(CA + BD)
c) DC + DA + BA + BC > 3(CA + BD)
d) DC + DA + BA + BC < CA − BD
Answer: b) DC + DA+ BA + BC < 2(CA + BD)
Explanation: The sum of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side. Therefore, the third side of a triangle is less than the sum of the other two sides.
In △AOB, BA < OA + OB ……………(I)
In △BOC, BC < OB + OC ……………(II)
In △COD, DC < OC + OD ……………(III)
In △DOA, DA < OD + OA ……………(IV)
Adding (I), (II), (III) and (IV).
BA + BC + DC + DA < OA + OB + OB + OC + OC + OD + OD + OA
⇒ DC + DA + BA + BC < 2OA + 2OB + 2OC + 2OD
⇒ DC + DA + BA + BC < 2(OA + OC + OB + OD)
∴ DC + DA + BA + BC < 2(CA + BD) [CA = OA + OC and BD = OB + OD]
4. In the right-angled triangle PQR where ∠P is the right angle. The midpoint of the hypotenuse QR is denoted as T. A line segment is drawn from point P to the midpoint T and extended to points S such that PT is equal to TS. Point S is then connected to point R as shown in the figure. The following statements are demonstrated:
(i) Triangles PTQ and RTS are congruent.
(ii) Triangles QPR and SRP are congruent.
(iii) ∠PTR is equal to 104° if ∠TRP is 33°.
(iv) The length of PT is greater than half of the length of SP.
(v) The length of PT is equal to half of the length of QR.
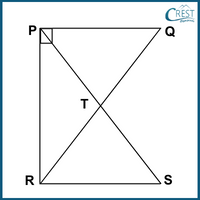
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
a) Only (ii) and (iii).
b) Only (ii), (iii) and (iv).
c) Only (iii) and (iv).
d) Only (iii), (iv)and (v).
Answer: c) Only (iii) and (iv).
Explanation: T is the midpoint of QR and PT = TS.
The statements are as follows:
(i) In △PTQ and △RTS,
QT = RT [T is the midpoint of QR]
∠PTQ = ∠PTQ [Vertically Opposite Angle]
PT = TS [Given]
△PTQ ≅ △RTS [By SAS Criterion]
Hence, statement (i) is correct.
(ii) In △QPR and △SRP,
△PTQ ≅ △RTS [By SAS Criterion]
△PTQ + △PTR ≅ △RTS + △PTR [Adding △PTR both side]
△QPR ≅ △SRP [△PTR is common to both △QPR and △SRP]
Hence, statement (ii) is correct.
(iii) In △PTR,
QR = SP [By CPCT, △QPR ≅ △SRP]
⇒ QT + RT = PT + TS [QR = QT + TR and SP = PT + TS]
⇒ RT + RT = PT + PT [Put QT = RT and PT = TS]
⇒ 2RT = 2PT
⇒ RT = PT
Angles opposite sides of equal length in a triangle are equal.
∴ ∠TPR = ∠TRP
⇒ ∠PTR + ∠TPR + ∠TRP = 180° [Sum of interior angle of a triangle is 180°.]
⇒ ∠PTR + 33° + 33° = 180° [From statement, ∠TRP = 33° and ∠TPR = ∠TRP]
⇒ ∠PTR = 114°
Hence, statement (iii) is not correct.
(iv) In △PSR,
SP = PT + TS
⇒ SP = PT + PT [Given: PT = TS]
⇒ SP = 2PT
⇒ PT = ½ SP
∴ The length of PT is equal to half of the length of SP.
Hence, statement (iv) is not correct.
(v) In △PQR and △PSR,
⇒ PT = ½ PS [As proved above in statement (iv).]
⇒ PT = ½ QR [QR = SP, By CPCT, △QPR ≅ △SRP]
∴ The length of PT is equal to half of the length of QR.
Hence, statement (v) is correct.
∴ Only statements (i), (ii) and (v) are correct. Only statements (iii) and (iv) are incorrect.
5. In △XYZ, the length of XY is (p − q), the length of ZY is √2pq and the length of ZX is √(p2 + q2). What is the value of the angle ∠ZYX?
a) 60°
b) 75°
c) 90°
d) 105°
Answer: c) 90°
Explanation: In △XYZ,
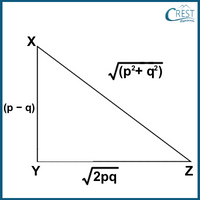
XY2 + ZY2 = (p − q)2 + (√2pq)2
⇒ XY2 + ZY2 = p2 + q2 − 2pq + 2pq
⇒ XY2 + ZY2 = p2 + q2 …………(i)
ZX2 = [√(p2 + q2)]2
⇒ ZX2= p2 + q2 …………(ii)
From (i) and (ii),
ZX2 = XY2 + ZY2
Which satisfy the Pythagoras' Theorem.
∴ Hence, ∠ZYX = 90°.







